Kim-Trump summit: A first step on the long road ahead


The new Trump-Kim joint agreement could prove a promising “memorandum of understanding.” However, it’s not just about denuclearization; it should also be about peace and US withdrawal from the Korean Peninsula.
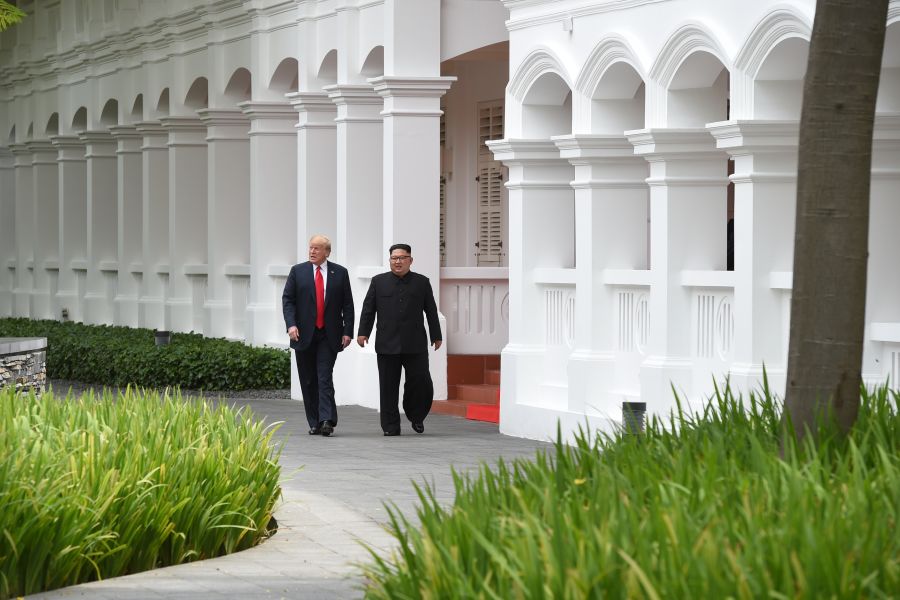
Here are the facts: Following hours of closed-door talks in Capella hotel in Singapore, US President Donald Trump and DPRK leader Kim Jong-un signed a joint four-point agreement: to establish new US-DPRK relations, a stable peace regime, a DPRK commitment to achieve the “complete denuclearization” of the Korean Peninsula, and the repatriation of the remains of US prisoners of war.
Unsurprisingly, the agreement does not include a firm “verifiable” and “irreversible” pledge by DPRK to abandon its nuclear weapon program. Yet, the Trump-Kim agreement is not a final deal, but a framework to pave the way to ongoing discussions. Consequently, it should be seen as a promising “memorandum of understanding.”
US and DPRK leaders have never met before. So technically, a state of war prevails between the two countries. For these two leaders to sit down, agree on their differences and outline a path to resolve them is a very big deal.
Nevertheless, a real peace and stability requires far more than a four-point agreement - a bilateral peace agreement and US withdrawal from the Korean Peninsula.
No stability without peace agreement
In the West, DPRK is customarily portrayed as a sort of a hermit kingdom and its leaders criticized. In reality, Pyongyang has long – and justifiably – seen US as an existential threat.
In 1951 – after Washington had lost its nuclear monopoly to the Soviet Union - the early setbacks in the Korean War prompted General MacArthur to consider using nuclear weapons against the Chinese and North Koreans – to use radioactive fallout zones to disrupt Chinese supply chains - until, he was dismissed by President Truman.
Nevertheless, between 1950 and 1953, the US subjected DPRK to a devastating bombing campaign, which destroyed 85 percent of the country’s buildings and caused one million civilians to die; more than the entire civilian deaths in World War II bombing of Germany and Japan, respectively. The scorched-earth policy set the standard of what was to come in Vietnam and the rest of Southeast Asia.
Ever since the 1953 Armistice Agreement, Washington has seen DPRK as a “rogue state.” Even with the Soviet Union, Washington supported “peaceful coexistence,” but with DPRK, only a “temporary ceasefire.” That’s the material basis for fears of imminent intrusion in Pyongyang.
In this status quo, Trump’s statement in the press conference that the US had agreed to stop playing “war games” with Pyongyang, referring to the joint military exercises with South Korea, is important. But while Trump added he wants to “bring our soldiers back home” from DPRK, he admitted it was “not part of the equation right now.”
Typically, the decision to cease the joint military exercises with South Korea was not included in the agreement. That’s vintage Trump. Only days before, he had nearly agreed to the G7 Summit communiqué, which fell apart amid the controversial aftermath. In the Trump world, deals are seldom fixed entities, but always subject to changing circumstances.
Last August, former US president Jimmy Carter who has negotiated with several DPRK leaders, noted that, for a long time, Pyongyang has sought a “peace treaty to replace the [1953] ceasefire.” In his experience, DPRK wanted peaceful relations with the US and regional neighbors.
In view of the long record of US-led regime changes and the recently-undermined Iran nuclear deal, that's not a futile concern.
No lasting peace without US withdrawal from the Korean Peninsula
In a televised 2013 New Year’s address, Kim Jong-un advocated "a radical turn in the building of an economic giant on the strength of science and technology by fanning the flames of the industrial revolution in the new century.” These economic efforts should “be manifested in the people’s standard of living.”
It was an appeal to the White House. But instead of seizing the transition in Pyongyang to work for the peace, President Obama opted for a Pentagon-led “pivot to Asia” that virtually ensured another half a decade of nuclear escalation. After Secretary of State Hillary Clinton’s outline for a Pentagon-led “pivot to Asia,” Obama did not want reconciliation with Pyongyang. Rather, the objective was to seize the opportunity to cooperate with the then-president of South Korea, Park Geun-hye, a conservative and the daughter of former president Park Chung-hee.
So, instead of rapprochement, Washington pushed for a Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) anti-ballistic missile system in South Korea. As far as Washington was concerned, THAAD would kill two birds with one stone: it would subdue Pyongyang and, if needed, it could be used to contain China. These plans, however, fell apart in early 2017, when president Park was impeached and sentenced to 24 years in prison. That paved the way to the presidency of the more moderate Moon Jae-in, who seeks reconciliation with DPRK.
Nevertheless, Park’s conservatives were able to postpone the repeal of the Operation Control agreement (OPCON), which allows the Pentagon - not Seoul - to control its military fate. The mission of the South Korea/US Combined Forces Command (CFC) is to “deter hostile acts of external aggression” South Korea by a “combined military effort.” The CFC is commanded by a US General and it has operational control (OPCON) over more than 600,000 active duty military personnel both countries.
President Park managed to defer the transfer to 2022. In the event of war, US interests will thus override the interests of South Koreans - in their own country.
The real obstacles
As a result, a true and lasting peace in the Korean Peninsula requires not just on the Trump-Kim deal and the implied talks.
It is also predicated on a Trump administration that will continue to support the talks, the nullification of impeachment efforts against the White House, minimal losses for the incumbents in the US mid-term elections, another Trump election triumph in 2020 – and continued support for the peace process in South Korea in the 2022 election.
It’s a very, very tall order. But in Singapore, Trump and Kim took the first, historical step to the right direction.
Dan Steinbock is an internationally recognized strategist of the multipolar world and the founder of Difference Group. He has served at the India, China and America Institute (US), the Shanghai Institutes for International Studies (China) and the EU Center (Singapore).