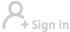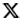Calligraphy offers strokes of tradition
Italian Sinologist delves deep into visual art form, searching for its true legacy and historical value, Fang Aiqing reports.
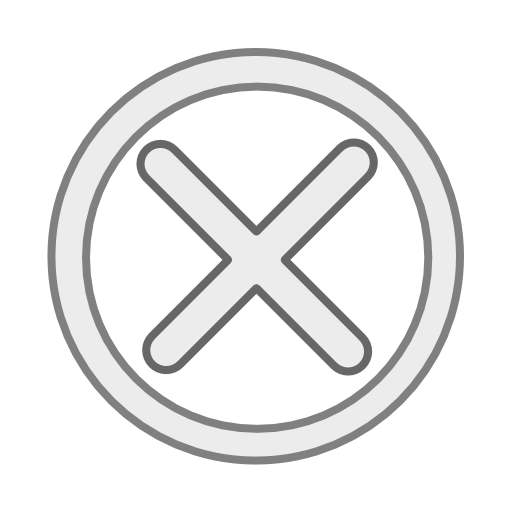


In the spring of 2019, upon his departure to Shaoxing in East China's Zhejiang province, Italian Sinologist Pietro De Laurentis explained to his mother that he was about to attend a Chinese calligraphy-themed seminar held in the hometown of "China's Leonardo da Vinci".
The professor of Chinese calligraphy history at the Guangzhou Academy of Fine Arts, Guangdong province, was referring to Wang Xizhi, a calligraphy master and intellectual from the Eastern Jin Dynasty (317-420). To the Italian scholar, Wang and da Vinci both represent their time and culture and expressed admiration and curiosity for the truth of nature in their improvisational creations.
Unfortunately, no confirmed authentic works of Wang have survived and the reliability of the some hundred ancient copies remains an inexhaustible research topic. Throughout history, the charm of Wang's calligraphy has been marveled at, accompanied by mysteries akin to those left by da Vinci.
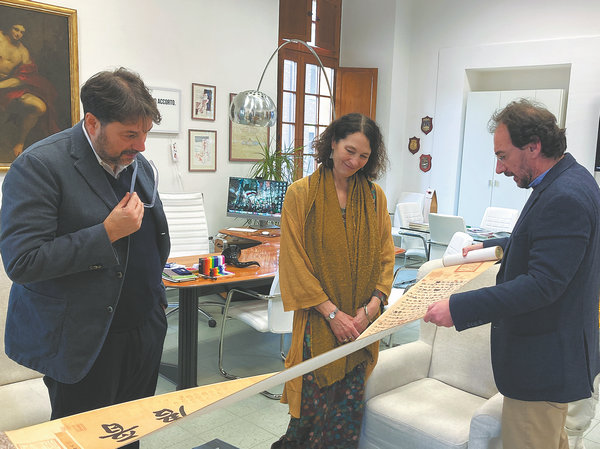
Despite this, De Laurentis, 47, is just one of numerous determined admirers searching for traces of Wang's true legacy within the great canon of historical archives, and he has indeed found a destination — the Xi'an Beilin Museum in Northwest China's Shaanxi province.
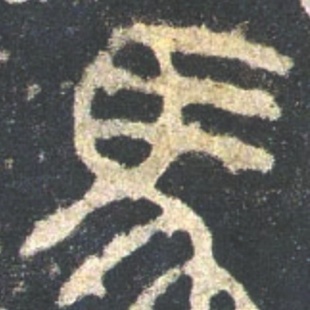
Among the more than 3,000 steles housed at the museum is a piece dating back to the Tang Dynasty (618-907) inscribed with 1,903 characters collated from a variety of Wang's works available at the time. In De Laurentis' perspective, this single stele is where the authentic charm of Wang's calligraphy lies.
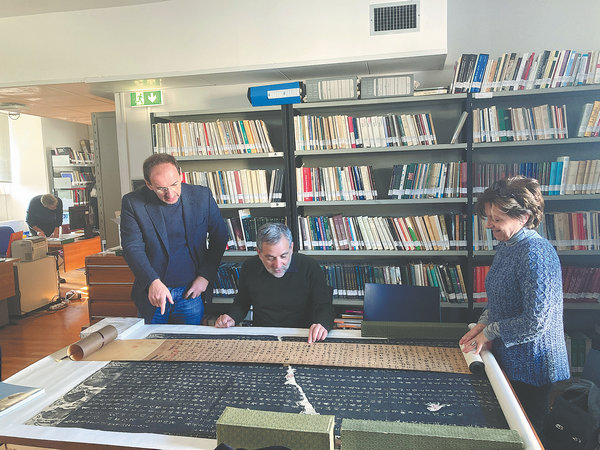

All along, language barriers have largely kept foreigners from fully appreciating the beauty of Chinese calligraphy, a visual art form often compared to modern abstract painting. Even contemporary Chinese natives accustomed to using pens and typing can easily get lost in the maze of brush calligraphy.
Yet the story behind this stele, which involves three major historical names, may offer a glimpse into Wang's historical influence.
During the early Tang Dynasty, Buddhist monk Xuanzang traveled westward to Central Asia and then studied in India. Seventeen years later in 645, he brought 657 titles of Buddhist scriptures back to his homeland. Since then, in the Tang capital of Chang'an, today's Xi'an, he dedicated himself to translating the scriptures.
In the summer of 648, a year before his passing, Li Shimin, known as Emperor Taizong, wrote a preface to Xuanzang's newly completed translation after spending over a month reading more than 100 volumes. Crown prince Li Zhi recorded this process.
These two royal texts in honor of Xuanzang and the dharma, together with the master's translation of the Heart Sutra, were transcribed onto a monument with characters collated from more than 2,000 scrolls of Wang's calligraphy that Emperor Taizong collected, mostly written in xingshu (semi-cursive) style.
Under the supervision of monk Huairen from the capital's Hongfu Monastery, the monument was finally completed in 673 and placed at the monastery, nine years after Xuanzang's passing.
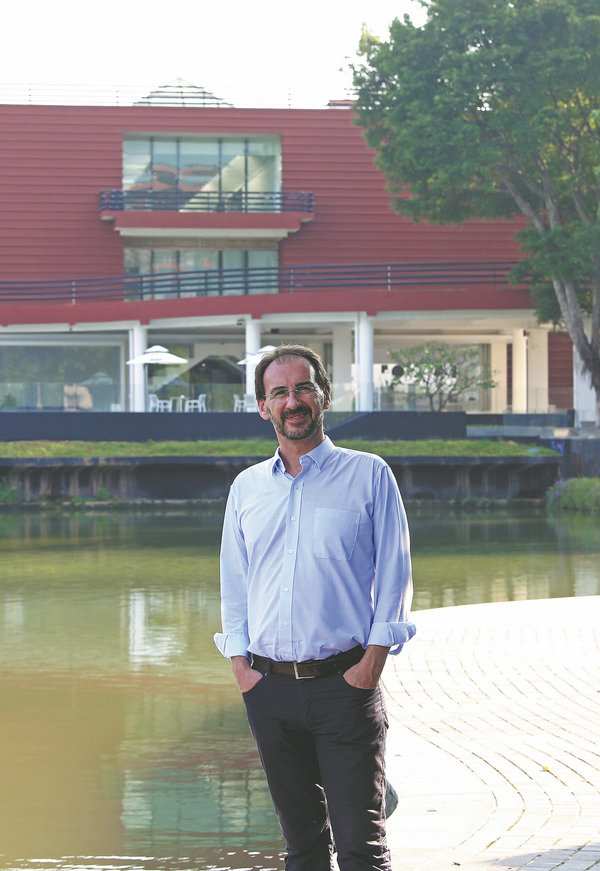

Three centuries after Wang's time, his calligraphy was showcased as a royal endorsement of the spread and adaptation of Buddhism in China. At a time when it was an extraordinary privilege to see Wang's calligraphy scrolls, this monument, standing in a public space, became a destination of pilgrimage, with copies and ink rubbings produced one after another.
"Despite its foreign origin, Chinese intellectuals admired Buddhism using Wang's calligraphy. It was only with the open-mindedness and rich imagination of the Tang Dynasty that such an idea could have possibly been conceived," says De Laurentis, who leads the Guangzhou academy's Centre for the Study of Handwriting Cultures and Artistic Exchange.
He published a monograph in English in 2021, which scrutinizes the monument's historical context and significance, as well as its artistic value.
"I would consider calligraphy a crucial aspect of the civilizational history of China and a highlight of Chinese culture, as it encompasses many aspects of the social concepts and daily lives of the ancient times."