Nation's economy showing signs of stability


This year, China's economy continues to demonstrate strong inertia and resilience in maintaining stable growth and quality enhancement. Amid internal and external pressures, China's macroeconomic policies have been characterized by proactive and well-targeted measures to bolster domestic demand, industrial upgrading and structural optimization, propelling the economy toward higher-quality and more sustainable growth.
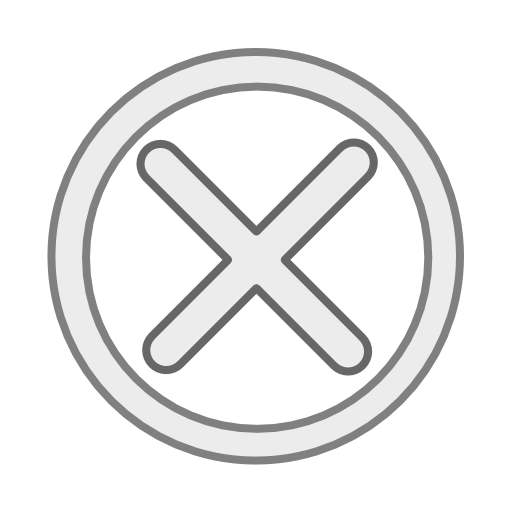
As the key engine of economic recovery, consumption has shown steady improvement supported by policy incentives and structural upgrades, with its contribution to GDP projected to increase significantly. Meanwhile, new quality productive forces are rapidly taking shape led by robust expansion in high-tech industries, which are becoming the catalyst for investment growth.
On the export side, diversification is taking hold. Businesses are expediting their transition up the value chain. Emerging markets, particularly those involved in the Belt and Road Initiative and ASEAN regions, are gaining in prominence, effectively mitigating uncertainties stemming from market volatility elsewhere.
At the macro-policy level, fiscal measures are characterized by coordinated efficiency. Deficit flexibility is being utilized to underpin growth and safeguard critical expenditures. Monetary policy is maintaining reasonable flexibility, retaining room for potential reserve requirement ratio reductions and interest rate cuts within the year to release liquidity and stabilize market expectations.
Fueled by multiple growth drivers, China's economy has exhibited steady advancement as endogenous momentum progressively strengthens, fortifying the groundwork for high-quality development.
As consumption remains the bedrock of a firm recovery, policy tailwinds reinforce domestic demand — the linchpin of China's economic resilience. Early 2025 saw intensive campaigns targeting automobiles, electronics and tourism, alongside accelerated trade-in subsidies nationwide, all aimed at reviving the consumer sector. Services consumption surged during the spring travel boom, while premium goods sales exceeded 20 percent year-on-year growth in May.
China's consumption upgrade trend has become more pronounced as emerging models inject vitality into the market. In addition to flourishing online consumption models, growing consumer preference for quality and diversity is facilitating rapid growth in high-value-added goods. Moreover, by enhancing household purchasing power, expanding quality supply and improving consumption environments, policies aim to fully unleash demand potential, promote economic development and elevate living standards.
Domestic consumption is poised for more robust growth in the second half of 2025.With the stabilization of employment and rise in household incomes, China's total retail sales are expected to achieve higher year-on-year growth than in 2024. In the services sector, upgraded demand will continue to be unleashed, emerging as a new engine for consumption.
Livelihood improvement measures — including pension increases and subsidies for low-income groups — will gradually enlarge middle-income populations and strengthen sustainable consumption capacity. Concurrently, systemic reforms in housing, healthcare and education will reduce households' high cost expenditure burdens, thereby boosting consumption appetites.
In 2025, consumption is projected to contribute over 60 percent of GDP growth, with its potential unfolding through three phases: policy stimulus, confidence recovery and endogenous expansion. Short-term stimuli yield quick results, while medium-term income upturns and structural reforms will shift consumption from rebound to active extension, cementing their pivotal role in China's high-quality development.
Innovation-driven industrial transformation is accelerating China's shift to next-generation productivity. Against the backdrop of a fluctuating external environment and weakening traditional drivers, China is rapidly cultivating new quality productive forces to achieve structural optimization, technology leadership and efficiency gains.
In May 2025, value-added industrial output above a designated size grew 5.8 percent year-on-year, with equipment manufacturing surging 9.0 percent and high-tech manufacturing up 8.6 percent. While traditional sectors including real estate are still undergoing realignment, this strong performance highlights how emerging sectors — particularly advanced equipment and intelligent manufacturing — are taking over to become the new engine of China's industrial growth.
The investment landscape is set for more proactive structural rebalancing. In 2025, ultra-long term special treasury bonds will prioritize major national projects and security capacity in key areas, while extending the implementation of large-scale equipment renewals and trade-ins of old consumer goods as well as providing policy support for manufacturing upgrades and investment in high-tech industries will bring about further stabilization.
Manufacturing and high-tech industry investments are anticipated to maintain significantly faster increases than overall investment in 2025. Guided by fiscal policy, infrastructure investment is expected to maintain moderate expansion at 5 to 6 percent. Notably, manufacturing and technology sectors will account for a rising share, balanced by real estate's declining proportion. This rebalancing will not only reduce structural reliance on property, but also strengthen China's endogenous growth drivers, injecting continuous momentum into high-quality development.
Quality-driven export upgrading, global footprint optimization and structural transformation are collectively enhancing China's economic resiliency. The rapid development of new quality productive forces serves as a strong underpinning for export growth alongside directing capital toward high-tech manufacturing and green industries. Through independent innovation and international brand-building initiatives, Chinese companies are establishing a stronger position in upscale global markets.
In addition, leading Chinese equipment manufacturers such as construction machinery and rail transportation are winning bids for major projects in countries involved in the Belt and Road Initiative with competitive cost effectiveness. China is witnessing a steady shift in export reliance from traditional markets toward developing economies. As the US share of China's exports has declined to approximately 12 percent, ASEAN has surpassed both the United States and Europe to become China's largest trading partner.
With short-term catalysts at play, China's export performance is expected to remain resilient in the latter half of 2025. If the US maintains its current tariff reduction arrangements, exports to its market would be stabilized. Concurrently, exporters may rush to ship abroad ahead of the tariff moratorium expiration, providing a temporary boost to third quarter performance.
Over an extended horizon, although aggregate export expansion may decelerate, compositional enhancements are projected to persist. Geographically, shipments will increasingly target emerging markets. Moreover, technical products and branded consumer goods shall become highlights, while the share of traditional labor-intensive exports may gradually decline. China's position in global value chains and export value-added content will steadily rise, providing strong support for high-quality foreign trade and economic development.
The policy framework exhibits strategic resolve by implementing synergistic measures to anchor expectations. Amid profound transformations in domestic and external environments, China's macroeconomic policies are maintaining a measured equilibrium between growth stabilization and risk prevention, reinforcing economic predictability and bolstering development confidence.
China's 2025 fiscal policy raises the deficit target to 4.0 percent of GDP, sending strong stabilizing signals to boost market confidence. April's national tax revenue growth of 1.9 percent year-on-year indicates successful transmission of earlier stimulus. The policy emphasizes special bond issuance and project implementation as well as preserves space to balance front-loaded stimulus moves with long-term buffers. Under constrained revenue increases, fiscal policy target spending on social welfare, infrastructure modernization and green transition will help enhance sustainability to build long-term growth potential.
Meanwhile, monetary policy is maintaining an accommodative stance, balancing short-term adjustments and medium-term stability. Through calibrated reserve requirement ratio cuts, structured instrument provisions and flexible liquidity operations, the central bank prioritizes support for technological innovation, green development and SME financing. Furthermore, it adheres to market-driven exchange rate mechanisms while reinforcing cross-border capital flows. With potential Fed rate cuts and subdued domestic inflation, the market anticipates additional interest rate cuts and RRR reductions this year to strengthen credit, reduce financing costs and stabilize market expectations.
In the second half of 2025, China's economy is poised to maintain a moderate recovery by leveraging domestic drivers. Despite external uncertainties, economic expansion is projected to remain balanced and sustainable under policy execution, likely achieving around 5 percent GDP growth target in line with official estimation.
The writer is chief economist at ICBC International Holdings Ltd.
The views do not necessarily reflect those of China Daily.