Killer particles travel the globe, study shows


Premature deaths of 2 million caused by PM2.5 linked to human consumption
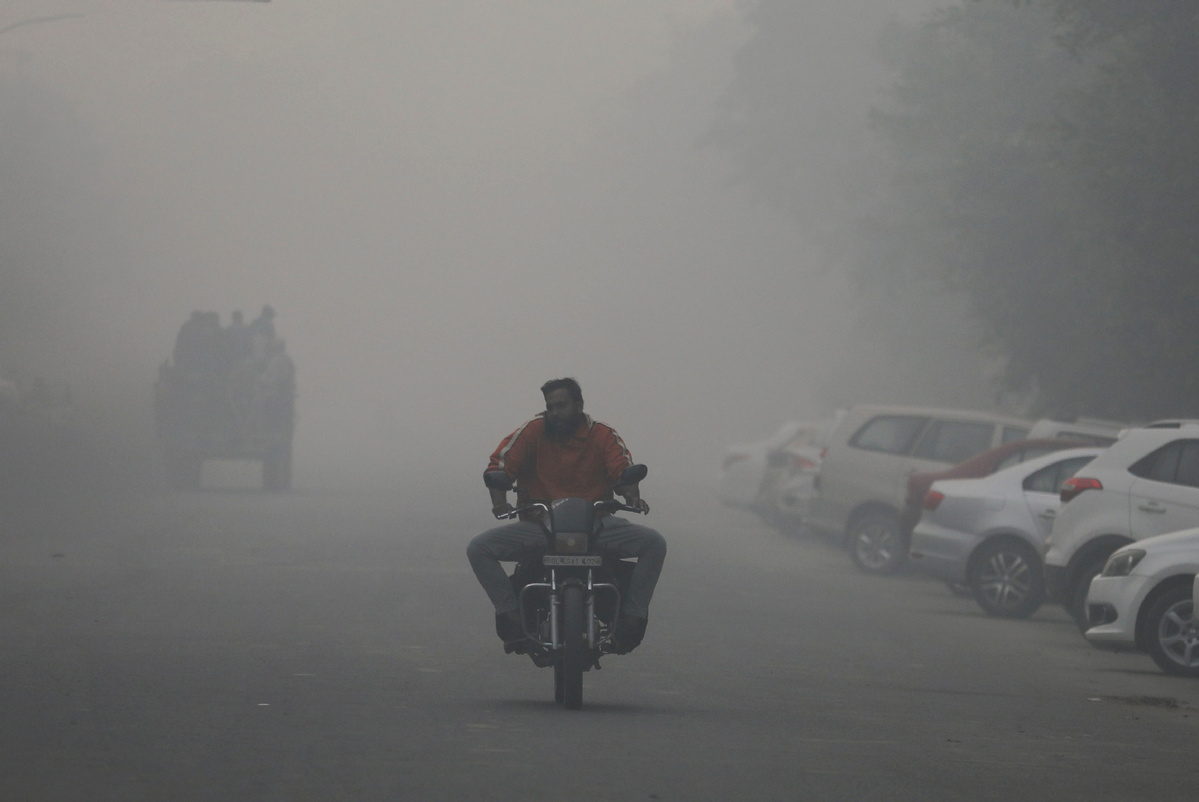
Microscopic particles in the air caused by pollution have contributed to the premature deaths of 2 million people a year, mainly in poor and developing countries, a study reveals.
The study, published by Nature Communications and led by Japanese researchers, shows half of the deaths have been caused by consumption in the world's greatest consuming countries.
Particulate pollution, or PM2.5, are particles 2.5 microns or smaller and invisible to the naked eye. Human hair, for example, is 50 microns on average.
Keisuke Nansai, one of the lead authors of the study, said that what makes the particles so dangerous is their size, which enables them to "bypass many of our body's defenses".
"They accumulate inside the lungs, where they severely increase the risk of ischemic heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke, lung cancer and lower respiratory tract infections," said Nansai, research director at the Material Flow Innovation Research Program in the National Institute for Environmental Studies in Japan.
The poor are especially vulnerable to PM2.5 and tend to die prematurely, he said.
"Most deaths are in developing countries, and without international coordination the situation will worsen."
While most countries acknowledge that they contribute to PM2.5 levels, there is little agreement on what form their financial responsibility should take, the study says.
It also says that PM2.5 particulate pollution caused by consumption is "far harder to measure" than that produced by factories and cars.
Manfred Lenzen, a University of Sydney professor who took part in the study, said: "This research shows that buying products sometimes means putting lives at risk. While we know that our carbon footprint jeopardizes our grandchildren's livelihoods, this research shows how our consumption harms other people's health in a much more immediate and direct way."
Air quality guidelines
In September, the World Health Organization issued "WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines", its first update on air quality in 15 years. "There is now a much stronger body of evidence to show how air pollution affects different aspects of health at even lower concentrations than previously understood," it said. "But here's what hasn't changed: Every year, exposure to air pollution is still estimated to cause millions of deaths and the loss of healthy years of life.
"The burden of disease attributable to air pollution is now estimated to be on a par with other major global health risks such as unhealthy diets and tobacco smoking."
In 2015, the World Health Assembly adopted a landmark resolution on air quality and health, recognizing air pollution as a risk factor for noncommunicable diseases including heart disease and cancer.
Determining the amount of PM2.5 caused by consumption is vital, Nansai said.
"Unlike direct production, which first affects the producing nation and then spreads across borders to neighboring nations, the PM2.5 caused by consumption may originate in distant nations and have negligible effects on consuming nations."
Cutting pollution from production emissions may require joint PM2.5 reduction measures in neighboring countries. Such collaboration, the study says, is unlikely among geographically distinct countries.
Nansai and his colleagues reasoned that understanding the impact that consumption of these nations has on PM2.5 levels would provide a reliable bench mark.
Using Eora, a database made nearly 10 years earlier to measure global supply chains, the study mapped out emissions from consumption alone.
The study shows that consumption by the world's greatest consuming countries, including the United States and the United Kingdom, causes a significant number of premature deaths in India, China and other faraway countries, whereas in neighboring countries-Mexico and Germany, for example-premature deaths caused by production are more common.
For most G20 members, the average age of premature deaths was nearly 70 years old. However, in countries such as South Africa and Saudi Arabia, premature infant death was so prevalent that the average age of premature deaths has fallen under 60. And the average age of premature deaths in India and Indonesia barely crossed this threshold.