China achieves first daytime laser ranging test in Earth-moon space

Chinese scientists have conducted a series of laser technology tests in space, aiming to verify the use of lasers in the country's ambitious space missions.
In a major milestone, an experimental satellite recently carried out the world's first daytime laser-ranging test in Earth-moon space, marking a breakthrough in China's deep-space orbital precision measurement capability, according to the Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology. The academy is a subsidiary of the State-owned China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp and the maker of the Tiandu 1 satellite.
The academy said in a news release Tuesday that the test was organized by the Deep Space Exploration Laboratory, a State-owned space research body based in Hefei, Anhui province. The test was conducted on April 26 and 27 with support from multiple domestic institutions, including the academy's Shanghai Institute of Satellite Engineering, the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Yunnan Observatories and Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, Sun Yat-sen University in Guangzhou, and the Beijing Aerospace Control Center.
Researchers from the laboratory said space-based laser ranging is a sophisticated method for measuring the distance between a ground station and a satellite equipped with retroreflectors. The technique involves transmitting laser pulses from the ground and timing how long they take to bounce back. It offers advantages such as high accuracy, long range, fast speed, and uninterrupted detection coverage. The method is crucial for scientific research and industries, including positioning and navigation.
Laser ranging in Earth-moon space, however, is extremely difficult due to the long distance and rapid movement of spacecraft. It is akin to targeting a single strand of hair from 10 kilometers away while maintaining precise tracking and signal capture.
Previous tests of laser ranging in Earth-moon space had been limited to nighttime because daytime sunlight interferes with the already weak echo signals from satellites, making detection and signal extraction nearly impossible.
The Deep Space Exploration Laboratory said the successful daytime test greatly extends the time frame in which laser ranging can be conducted and proves the engineering feasibility of the technology. It is expected to enhance China's navigation and positioning capabilities in cislunar space and support key deep-space projects, including the International Lunar Research Station.
Tiandu 1 is one of two technology demonstration satellites operated by the laboratory. It was launched in March 2024 and is currently in a round-trip orbit between Earth and the moon.
zhaolei@chinadaily.com.cn
?
- China achieves first daytime laser ranging test in Earth-moon space
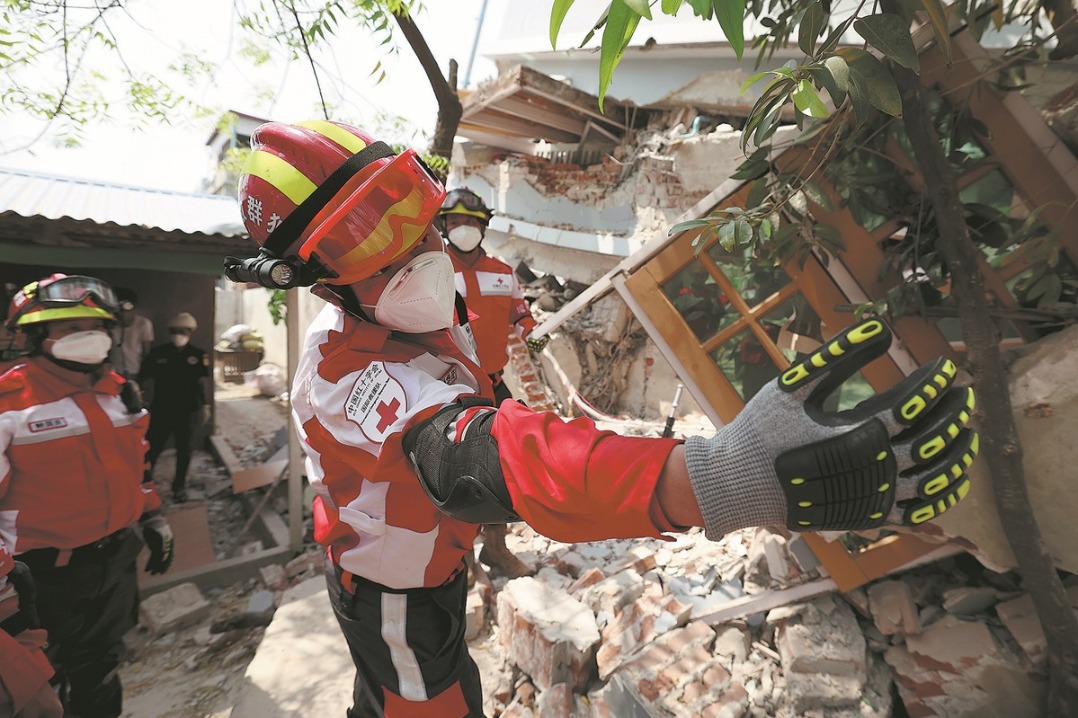
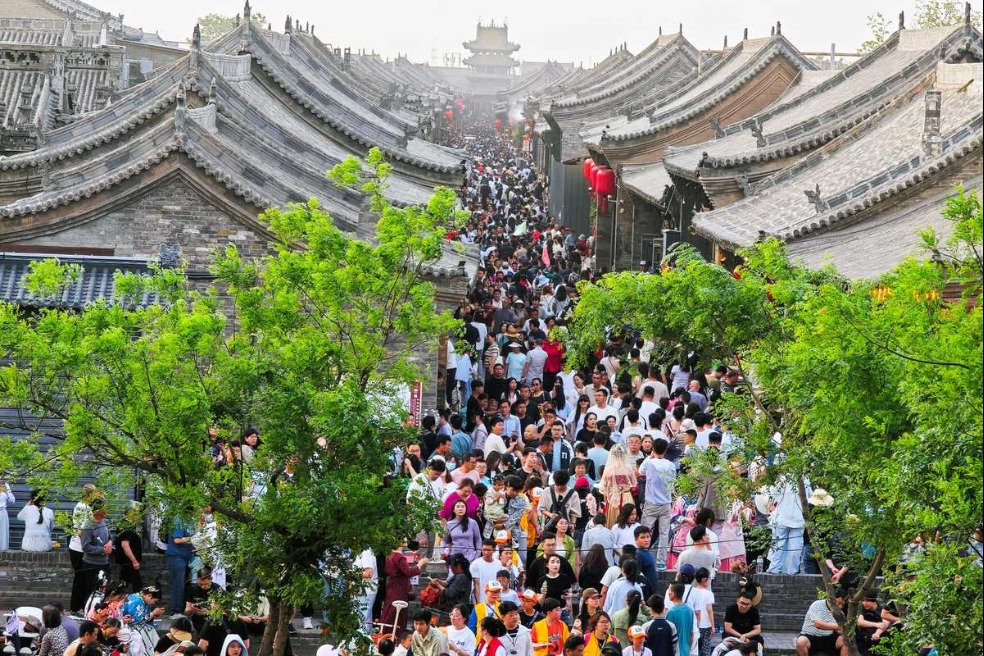
- Ten photos from across China: May 2 - 8
- PLA Honor Guard set for Red Square parade
- Hainan a magnet for Russian tourists
- Venezuelan expat dedicated to promoting Tianjin cross-talk in Spanish-speaking world
- Facing aging society, China boosts geriatric care at major hospitals