Reducing climate impact on human health
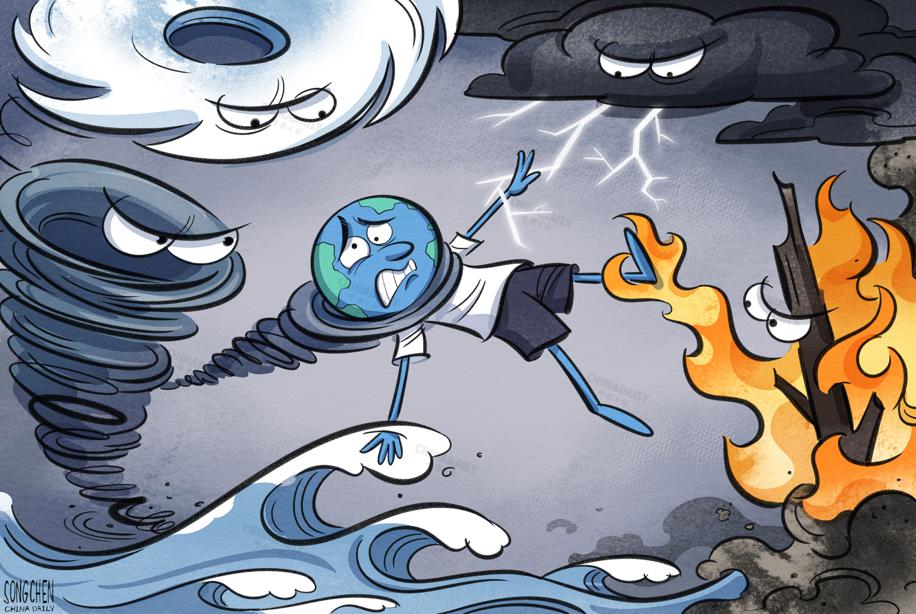


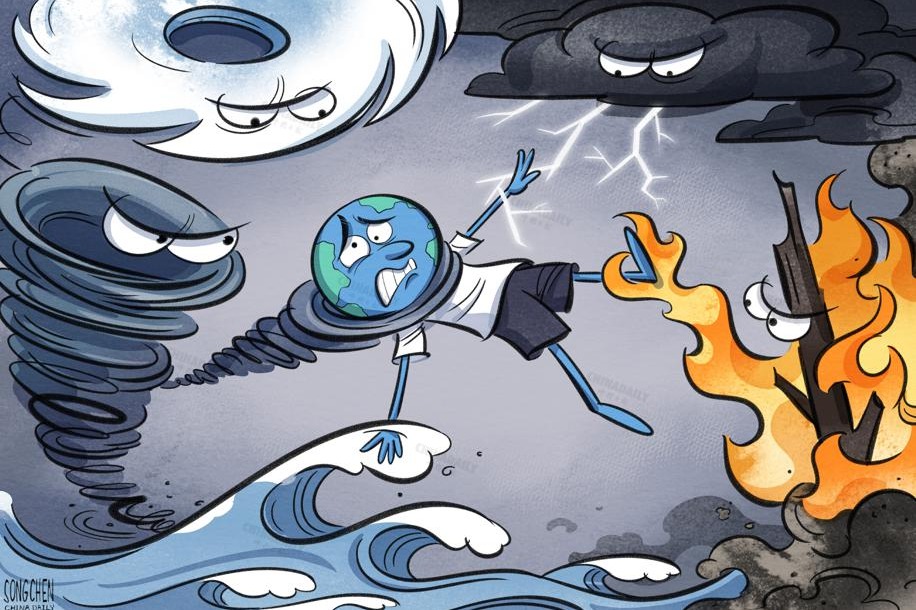
The increasing frequency of extreme weather and other climate-related events caused by climate change is affecting human health in multiple ways. Climate change is increasing the spread of infectious diseases: by directly impacting communicable diseases and indirectly altering vectors. Rising temperatures and pollution are directly impacting human health by contributing, through complex mechanisms, to increased incidences of cardiovascular, respiratory and other diseases. Changes in vectors due to climate change are influencing the transmission of infectious diseases. While frequent extreme weather events, leading to major natural disasters, also pose significant mental health risks, environmental effects of climate change like reduced crop yield and water shortage threaten people's health and livelihoods.
For instance, changes in temperature patterns and atmospheric pressure, along with extreme weather events like heatwaves and cold spells, directly threaten human cardiovascular and respiratory systems, while heat waves overload the human thermoregulatory mechanism and exacerbate preexisting organ and tissue dysfunction, thereby increasing the risk of respiratory and circulatory diseases. Cold spells, on their part, induce vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels), raising blood pressure and increasing platelet count, and cholesterol and fibrinogen levels, all of which aggravate cardiovascular and cerebrovascular dysfunction.
Cases of mosquito-borne diseases including dengue and malaria are increasing at a rapid pace across most parts of the world. Shifts in environmental variables, including temperatures, relative humidity and precipitation, combined with growing human mobility have made vectors even more resistant, leading to rising cases even in regions earlier untouched by certain diseases (in high-altitude regions for instance). Besides, increasing air pollution, wildfires and prolonged exposure to extreme heat is increasing airborne allergen concentrations, thereby impairing people's respiratory system. Climate change is also prolonging the pollen season and increasing pollen allergenicity, while extreme weather events like thunderstorms, with frequent lightning strikes, are fracturing pollens into smaller particles, increasing the risk of asthma attacks.
To address climate change-related health risks, countries worldwide are taking proactive, complementary measures. However, to overcome all the challenges created by climate change, countries have to implement long-term measures to transform their economies by making their power and industrial sectors eco-friendly and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In fact, many countries have intensified their efforts to address climate-related health risks, with the World Health Organization according priority to addressing the climate-health challenges, playing a leadership role in highlighting the impacts of climate change on human health.
Through initiatives like the framework for building climate-resilient and low-carbon health systems, the WHO has been urging countries to integrate health adaptation measures into their climate-action strategy and allot more funds to combat climate change.
The WHO also spearheads the "Alliance for Transformative Action on Climate and Health" to provide targeted support for health ministries of countries. The initiative focuses on fostering cross-sectoral collaboration, updating technical guidelines, organizing practical training programs, supporting project preparation and implementation, and securing dedicated climate-health financing.
The ATACH initiative has already established effective operational mechanisms in areas such as financial support mobilization, scientific research collaboration and pilot project implementation. These efforts have significantly advanced both research and practical applications in the climate-health field while strengthening interdisciplinary and cross-sectoral cooperation, turning the initiative into a robust support platform for advancing the global climate-health agenda.
Moreover, the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (or COP) has progressively integrated public health issues into the critical discussed topics and advanced numerous public health policies combining climate adaptation and mitigation strategies. COP28 was a milestone as it held the first "Health Day", and adopted the "COP28 UAE Declaration on Climate and Health", which calls on all countries to address health threats including extreme heat, air pollution, infectious diseases and food insecurity while placing health at the core of their climate action.
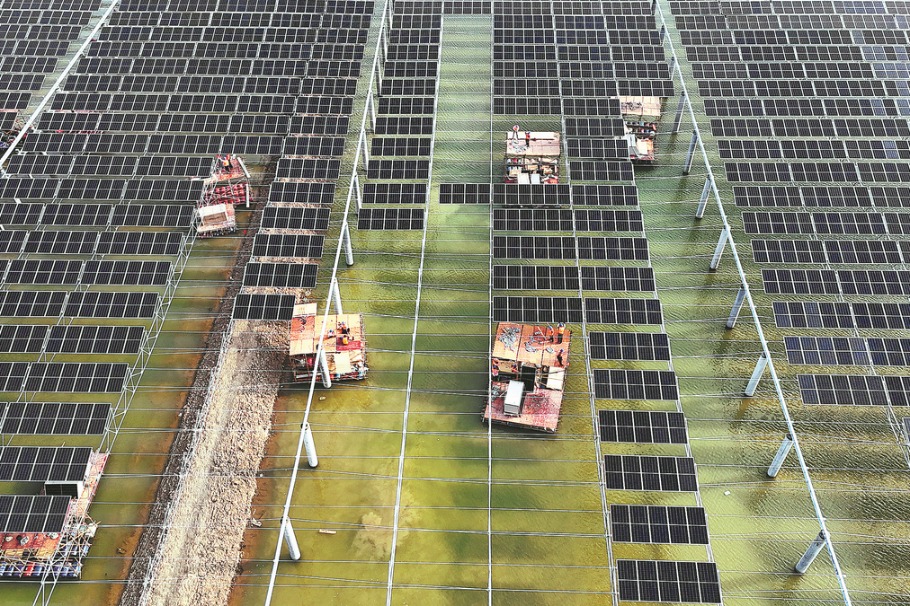
The COP28 agreement also achieved a breakthrough by calling for "transitioning away from all fossil fuels", highlighting renewable energy and low-carbon technologies' crucial role in reducing air pollution.
Before the opening of COP29 in Azerbaijan last year, the WHO released two key documents — the COP29 Special Report on Climate Change and Health: Health is the Argument for Climate Action and Quality criteria for integrating health into Nationally Determined Contributions — which emphasize the importance of integrating public health considerations into climate action.
The international community has embraced a health-centered climate action framework, integrating adaptation and mitigation strategies. By further fostering cross-sector collaboration, promoting innovation and deepening global cooperation on climate action, the international community can more systematically address the climate-health challenge. For that, however, the industrialized countries have to fulfill their promise of contributing to the global climate fund and transferring technologies to developing countries to help the latter better combat climate change.


The views don't necessarily reflect those of China Daily.
If you have a specific expertise, or would like to share your thought about our stories, then send us your writings at opinion@chinadaily.com.cn, and comment@chinadaily.com.cn.